Selection Sort in C++ Programming
Sorting in C++
In this lesson, we will understand what is Selection Sort in C++ Programming along with some examples.
What is Selection Sort in C++?
A Selection Sort is a sorting technique used in C++ to sort elements of an array in ascending or descending order.
In this sorting technique, we will find the smallest element from the array and place it in the first position of the array. After that, we will take the second smallest number from the array and place it in the second position of the array in this way we will sort the entire array in ascending order.
To clearly understand the selection sorting technique, let's go through its algorithm step by step with an example.
Selection Sort Visualization
Suppose we have seven numbers stored in an array as shown below.
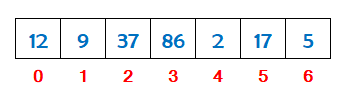
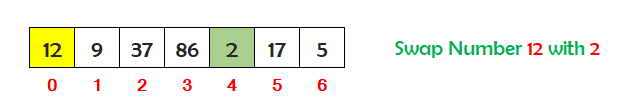
Find the smallest number stored in the array between index 0 and 6. So the smallest number is 2. Check if the number at index 0 is greater than the smallest number at index 4. If yes, then swap the numbers.
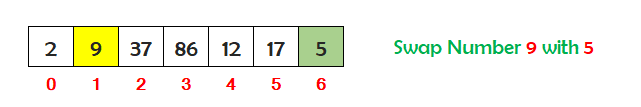
Now find the second smallest number stored in the array between index 1 and 6. So the second smallest number is 5. Check if the number at index 1 is greater than the second smallest number at index 6. If yes, then swap the numbers.
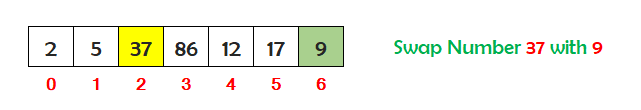
Now find the third smallest number stored in the array between index 2 and 6. So the third smallest number is 9. Check if the number at index 2 is greater than the third smallest number at index 6. If yes, then swap the numbers.
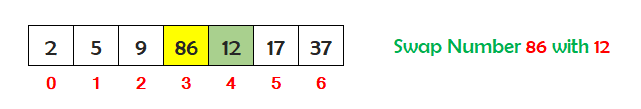
Now find the fourth smallest number stored in the array between index 3 and 6. So the fourth smallest number is 12. Check if the number at index 3 is greater than the fourth smallest number at index 4. If yes, then swap the numbers.
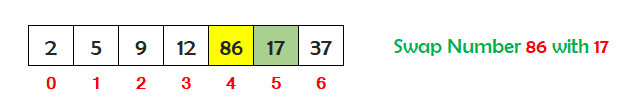
Now find the fifth smallest number stored in the array between index 4 and 6. So the fifth smallest number is 17. Check if the number at index 4 is greater than the fifth smallest number at index 5. If yes, then swap the numbers.
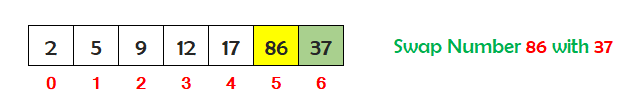
Now find the sixth smallest number stored in the array between index 5 and 6. So the sixth smallest number is 37. Check if the number at index 5 is greater than the sixth smallest number at index 6. If yes, then swap the numbers.
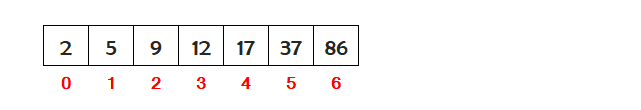
So we can see that the entire array has sorted in ascending order.
Algorithm for Selection Sort
An algorithm is the steps used to implement the selection sort in a c++ program.
Assume we have N numbers stored in an array. To implement the selection sort on N numbers, the steps are as follows.
- Define an array to store N numbers for selection sort. Suppose we have defined an array with the name num.
- Run an outer loop i from 0 to N-1 to repeat the process of selection sort.
- Store the value of i in a variable snp (smallest number position). For example snp=i.
- Run an inner loop j inside the body of the outer loop i for selection sort from i+1 to N.
- Inside the body of the inner loop j, check if the value at num[j] is smaller than the value at num[snp].
- If the value at num[j] is smaller than value at num[snp] then store the value of j to snp. For example snp=j.
- Outside the body of the inner loop j check if the value at num[i] is greater than that value at num[snp]. If yes, then swap the numbers.
- Now print the sorted array on the screen outside the body of the outer loop i.
C++ Program for Selection Sort
A C++ program to sort an array of numbers in ascending order using the selection sort technique.
Selection Sort (List of Numbers in Ascending Order)
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// define an array
int num[]= {12,9,37,86,2,17,5};
int i,j,t,snp;
cout<<"Array before Selection Sort"<<endl;
for(i=0; i<7; i++)
{
cout<<num[i]<<" ";
}
// run an outer loop i from 0 to N-1 to repeat the process of selection sort
for(i=0; i<6; i++)
{
// smallest number position
snp=i;
// run an inner loop j for selection sort from i+1 to N
for(j=i+1; j<7; j++)
{
// now check if the value at num[j] is smaller than value at num[snp]
if(num[j]<num[snp])
{
// if the value is smaller, then store the value of j to snp
snp=j;
}
}
// outside the body of inner loop j check if num[i]>num[snp]. If yes then swap the numbers
if(num[i]>num[snp])
{
t=num[i];
num[i]=num[snp];
num[snp]=t;
}
}
// print the sorted array
cout<<"\n\nArray after Selection Sort\n";
for(i=0; i<7; i++)
{
cout<<num[i]<<" ";
}
return 0;
}Output
Array before Selection Sort 12 9 37 86 2 17 5 Array after Selection Sort 2 5 9 12 17 37 86
A C++ program to sort an array of numbers in descending order using the selection sort technique.
Selection Sort (List of Numbers in Descending Order)
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// define an array
int num[]= {12,9,37,86,2,17,5};
int i,j,t,lnp;
cout<<"Array before Selection Sort"<<endl;
for(i=0; i<7; i++)
{
cout<<num[i]<<" ";
}
// run an outer loop i from 0 to N-1 to repeat the process of selection sort
for(i=0; i<6; i++)
{
// largest number position
lnp=i;
// run an inner loop j for selection sort from i+1 to N
for(j=i+1; j<7; j++)
{
// now check if the value at num[j] is greater than value at num[lnp]
if(num[j]>num[lnp])
{
// if the value is greater, then store the value of j to lnp
lnp=j;
}
}
// outside the body of inner loop j check if num[i]<num[lnp]. If yes then swap the numbers
if(num[i]<num[lnp])
{
t=num[i];
num[i]=num[lnp];
num[lnp]=t;
}
}
// print the sorted array
cout<<"\n\nArray after Selection Sort\n";
for(i=0; i<7; i++)
{
cout<<num[i]<<" ";
}
return 0;
}Output
Array before Selection Sort 12 9 37 86 2 17 5 Array after Selection Sort 86 37 17 12 9 5 2
A C++ program to sort an array of strings in ascending order using the selection sort technique.
Selection Sort (List of Strings in Ascending Order)
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// define an array
string num[]= {"Squirrel","Dog","Panda","Lion","Bear","Tiger","Rabbit"};
string t;
int i,j,snp;
cout<<"Array before Selection Sort"<<endl;
for(i=0; i<7; i++)
{
cout<<num[i]<<" ";
}
// run an outer loop i from 0 to N-1 to repeat the process of selection sort
for(i=0; i<6; i++)
{
// smallest string position
snp=i;
// run an inner loop j for selection sort from i+1 to N
for(j=i+1; j<7; j++)
{
// now check if the value at num[j] is smaller than value at num[snp]
if(num[j].compare(num[snp])<0)
{
// if the value is smaller, then store the value of j to snp
snp=j;
}
}
// outside the body of inner loop j check if num[i]>num[snp]. If yes then swap the strings
if(num[i].compare(num[snp])>0)
{
t=num[i];
num[i]=num[snp];
num[snp]=t;
}
}
// print the sorted array
cout<<"\n\nArray after Selection Sort\n";
for(i=0; i<7; i++)
{
cout<<num[i]<<" ";
}
return 0;
}Output
Array before Selection Sort Squirrel Dog Panda Lion Bear Tiger Rabbit Array after Selection Sort Bear Dog Lion Panda Rabbit Squirrel Tiger
Selection Sort Program Explanation
The explanation of the above program (List of Numbers in Ascending Order) is given below in details.
Explanation
Array before Selection Sort
12 9 37 86 2 17 5
The outer loop i starts running from 0 to 5
When i = 0
snp = 0
The inner loop j starts running from 1 to 6
When j = 1
Array is : 12 9 37 86 2 17 5 Check if 9<12 Yes 9<12 then store the value of j to snp
snp = 1
When j = 2
Array is : 12 9 37 86 2 17 5 Check if 37<9 No
When j = 3
Array is : 12 9 37 86 2 17 5 Check if 86<9 No
When j = 4
Array is : 12 9 37 86 2 17 5 Check if 2<9 Yes 2<9 then store the value of j to snp
snp = 4
When j = 5
Array is : 12 9 37 86 2 17 5 Check if 17<2 No
When j = 6
Array is : 12 9 37 86 2 17 5 Check if 5<2 No
The inner loop ends. Now check if 12>2. If yes then swap the numbers
Array is : 2 9 37 86 12 17 5
When i = 1
snp = 1
The inner loop j starts running from 2 to 6
When j = 2
Array is : 2 9 37 86 12 17 5 Check if 37<9 No
When j = 3
Array is : 2 9 37 86 12 17 5 Check if 86<9 No
When j = 4
Array is : 2 9 37 86 12 17 5 Check if 12<9 No
When j = 5
Array is : 2 9 37 86 12 17 5 Check if 17<9 No
When j = 6
Array is : 2 9 37 86 12 17 5 Check if 5<9 Yes 5<9 then store the value of j to snp
snp = 6
The inner loop ends. Now check if 9>5. If yes then swap the numbers
Array is : 2 5 37 86 12 17 9
When i = 2
snp = 2
The inner loop j starts running from 3 to 6
When j = 3
Array is : 2 5 37 86 12 17 9 Check if 86<37 No
When j = 4
Array is : 2 5 37 86 12 17 9 Check if 12<37 Yes 12<37 then store the value of j to snp
snp = 4
When j = 5
Array is : 2 5 37 86 12 17 9 Check if 17<12 No
When j = 6
Array is : 2 5 37 86 12 17 9 Check if 9<12 Yes 9<12 then store the value of j to snp
snp = 6
The inner loop ends. Now check if 37>9. If yes then swap the numbers
Array is : 2 5 9 86 12 17 37
When i = 3
snp = 3
The inner loop j starts running from 4 to 6
When j = 4
Array is : 2 5 9 86 12 17 37 Check if 12<86 Yes 12<86 then store the value of j to snp
snp = 4
When j = 5
Array is : 2 5 9 86 12 17 37 Check if 17<12 No
When j = 6
Array is : 2 5 9 86 12 17 37 Check if 37<12 No
The inner loop ends. Now check if 86>12. If yes then swap the numbers
Array is : 2 5 9 12 86 17 37
When i = 4
snp = 4
The inner loop j starts running from 5 to 6
When j = 5
Array is : 2 5 9 12 86 17 37 Check if 17<86 Yes 17<86 then store the value of j to snp
snp = 5
When j = 6
Array is : 2 5 9 12 86 17 37 Check if 37<17 No
The inner loop ends. Now check if 86>17. If yes then swap the numbers
Array is : 2 5 9 12 17 86 37
When i = 5
snp = 5
The inner loop j starts running from 6 to 6
When j = 6
Array is : 2 5 9 12 17 86 37 Check if 37<86 Yes 37<86 then store the value of j to snp
snp = 6
The inner loop ends. Now check if 86>37. If yes then swap the numbers
Array is : 2 5 9 12 17 37 86
The outer loop ends
Array after Selection Sort
2 5 9 12 17 37 86



