String in C++ Programming
String in C++
In this lesson, we will understand what is String in C++ Programming along with some examples.
What is String in C++
A String is a sequence of characters. In C++ programming, a string can be created in two ways.
- By using C-Style Character String.
- By using standard String Class.
C-Style Character String
A C-Style Character String uses a Character Array to store sequence of characters.
Declaration Syntax of a Character Array in C++
char variable_name[size]Here, size is the maximum number of characters that can be store in the character array.
Example
char a[15];The above character array can store a string up to 15 characters long. You can use any size that fits your requirement.
Declaration and Initialization of a Character Array in C++
In C++ programming a character array can be declared and initialized in 3 ways. Let's see all the three examples.
Example 1
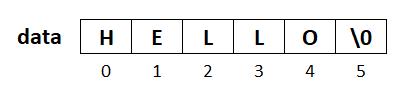
char data[]= {'H','E','L','L','O','\0'};In Example 1, we have declared a character array named data and initialize it with the string HELLO. We put a null character (‘\0’) at the end, which specifies the end of the string. So, the actual size of the array is 6, including the null character.
Example 2
char data[]= "HELLO";In Example 2, we have used double quotes (") to initialize the word HELLO in the character array. Here we don’t have to specify the null character (‘\0’) because it is added automatically.
Thus, both the examples will look like as given in the picture below.
Example 3
char data[10]= "HELLO";In Example 3, we have mentioned the size 10 and then use the quotes (") to initialize the word HELLO in the character array. In this case the array will look like as given in the picture below.
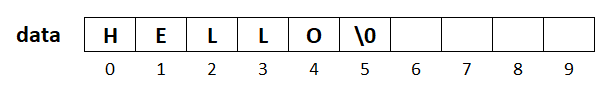
Store Characters in a Character Array
We can store character in a character array using 3 methods:
- Store characters one by one.
- Store a single word string using cin statement.
- Store a multi-word string using cin.get() statement.
- Store a multi-word string using gets() function.
Let’s see all the examples one by one.
Example 1 (store characters one by one)
data[0]='H';
data[1]='E';
data[2]='L';
data[3]='L';
data[4]='O';
data[5]='\0';
Example 2 (store a single word string using cin statement)
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char data[20];
cout<<"Enter Name ";
cin>>data;
return 0;
}In example 2, we have used cin statement to take a single word string input from the user.
Example 3 (store a multi-word string using cin.get() statement)
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char data[20];
cout<<"Enter Full Name ";
cin.get(data,20);
return 0;
}In example 3, we have used a cin.get() statement to take a multi-word string input from the user. In cin.get() statement, the first argument is the name of the character array and the second argument is the size of the character array.
Example 4 (store a multi-word string using gets() function)
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char data[20];
cout<<"Enter Full Name ";
gets(data);
return 0;
}In example 4, we have used gets() function to take multi-word string input from the user. To use the gets() function we have to include stdio.h header file in our program.
Display Characters from a Character Array
To display all characters from a character array we can use either cout statement or puts() function.
Example 1 (display characters using cout statement)
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char data[20];
char city[20];
cout<<"Enter Name ";
gets(data);
printf("Enter City ");
gets(city);
cout<<"Name: "<<data<<" City: "<<city;
return 0;
}Output
Enter Name Allen Smith Enter City California Name: Allen Smith City: California
Note: In the above example, we have used the cout statement and insertion operator << to print the name and city on the same line on the screen.
Example 2 (display characters using puts() function)
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char data[20];
char city[20];
cout<<"Enter Name ";
gets(data);
printf("Enter City ");
gets(city);
cout<<"Name: ";
puts(data);
cout<<"City: ";
puts(city);
return 0;
}Output
Enter Name Allen Smith Enter City California Name: Allen Smith City: California
Note: In the above example, the puts() function print the character array on the screen and then break the line automatically. Using puts() function, we cannot print multiple outputs on the same line. In order to do so, we have to use the cout statement instead of puts() function.
Access Individual Characters from a Character Array
We can access individual characters from a character array using for, while or do while loop.
Example
Program to input a word and print individual characters on separate lines.
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char data[20];
int i;
cout<<"Enter Name ";
gets(data);
for(i=0; data[i]!='\0'; i++)
{
cout<<data[i]<<endl;
}
return 0;
}Output
Enter Name Dremendo D r e m e n d o
In the above example, we have run a 'for loop' from 0 until we get null (‘\0’) and then print the individual characters on the screen using cout statement on separate lines.
Two Dimensional Character Array in C++
A Two Dimensional character array is used to store the list of strings. For example a list of country names, list of fruit names, etc.
Declaration Syntax of a Two Dimensional Character Array in C++
char variable_name[row_size][column_size];Here row_size is the number of rows we want to create in a 2D character array and, column_size is the number of maximum characters we want to store in each row.
Example
char list[5][10];The above 2D character array named list can store 5 strings having maximum 10 characters in each string.
Declaration and Initialization of a Two Dimensional Character Array in C++
In C++ programming a two dimensional character array can be declared and initialized in two ways. Let’s see both ways.
Example 1: (with row and column size mentioned)
char list[5][10]= {"Apple", "Banana", "Cherry"};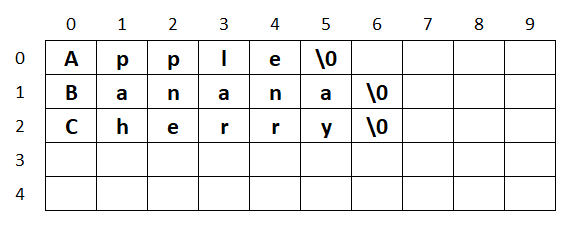
Example 2: (with only column size mentioned)
char list[][10]= {"Apple", "Banana", "Cherry"};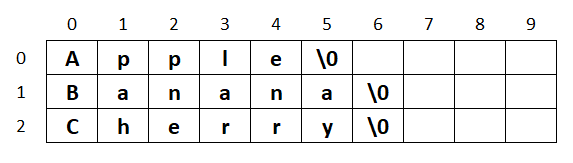
Store and Access Strings in a Two Dimensional Character Array
We can store and access string in 2D character array using for loop. Let’s see the example given below.
Example
Program to store and display the names of 3 fruits in a 2D character array.
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char list[3][10];
int r;
//store the name 3 fruits
cout<<"Enter 3 fruits name"<<endl;
for(r=0; r<3; r++)
{
gets(list[r]);
}
//access the name of 3 fruits from the array
cout<<"\nNames of 3 fruits are"<<endl;
for(r=0; r<3; r++)
{
cout<<list[r]<<endl;
}
return 0;
}Output
Enter 3 fruits name Apple Banana Cherry Names of 3 fruits are Apple Banana Cherry
Note: To store and access the above 2D character array we just need to specify the array name along with the row index in square brackets [ ] as shown in the above example.
Standard String Class
The string class type provided in the C++ as a part of the standard library can be used to store a string.
Declaration Syntax of a string class type object
string str;Here, str is the object of string class type.
Declaration and Initialization of a string class type object
string str="Hello World";Here, we have declared a string type object str and initialize it with the string Hello World.
Input and Print String using getline() Function
We can use getline() function to take input in a string object, and print the string using cout statement. See the example given below.
Example
Program to input any string from the user and print it on the screen.
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str;
cout<<"Enter any string"<<endl;
getline(cin,str);
cout<<"You have entered: "<<str;
}Output
Enter any string Hello World You have entered: Hello World
The getline() function requires two arguments, first an input stream and second the name of the string object in which we want to take input.
Access Individual Characters from String Object
We can access individual characters from a string object using at() function.
Example
Program to input a word in a string object and print individual characters on separate lines using at() function.
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str;
int i;
cout<<"Enter a word ";
getline(cin,str);
for(i=0; i<str.size(); i++)
{
cout<<str.at(i)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}Output
Enter a word Hello H e l l o
Here, we have first input a word from the keyboard. After that, we run a loop from 0 to less than the size of the string using size() function and then print all the individual characters on the screen using at() function.



