Doubly Linked List in Java Programming
User-Defined Data Structures in Java
In this lesson, we will understand what is Doubly Linked List in Java Programming and how to create them along with some examples.
What is Doubly Linked List in Java
Just like Singly Linked List, a Doubly Linked List in java is a user-defined data structure in which data is stored as an object called a node. Each node has three parts in a doubly linked list: the data, the previous, and the next.
The data part stores the data, the previous part stores the memory address of the previous node, and the next part holds the memory address of the next node, as shown in the image below.
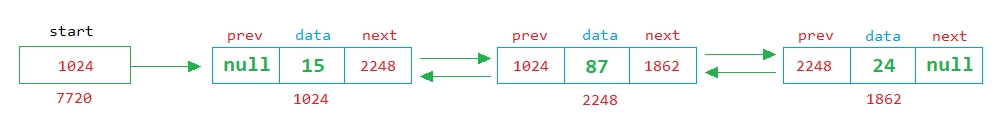
In the above image, the start is a variable that stores the memory address of the first node.
The first node has three parts: the data, the prev and the next. The prev and the next parts stores the memory address of the previous and next nodes.
In a doubly linked list, data are not stored in a contagious memory location. A new node can be created anywhere in the memory at runtime.
We can create as many nodes as we want by linking the newly created node with the last node.
Structure of a Doubly Linked List Program
Below we have given the complete structure of a doubly linked list program in java, along with all the operations we will perform.
Example
import java.util.Scanner;
// define Node class
class Node
{
public int data = 0;
public Node prev = null;
public Node next = null;
}
public class DoublyLinkedList
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node start=null,newnode,temp,rn;
int ch,n,x,c,f;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
for(;;) // An infinite loop
{
System.out.println("\n1. Add");
System.out.println("2. Display");
System.out.println("3. Insert Before");
System.out.println("4. Insert After");
System.out.println("5. Count");
System.out.println("6. Search");
System.out.println("7. Delete");
System.out.println("8. Reverse");
System.out.print("Enter Choice: ");
ch=sc.nextInt();
switch(ch)
{
case 1: // for add operation
break;
case 2: // for display operation
break;
case 3: // for insert before operation
break;
case 4: // for insert after operation
break;
case 5: // for node count operation
break;
case 6: // for node serach operation
break;
case 7: // for delete operation
break;
case 8: // for reverse
break;
default: // default case for wrong choice input
System.out.println("Invalid Choice");
}
}
}
}The above program shows how a doubly linked list program will look with all the operations on it. Now we will discuss each part of the above program and the program required to be written in each case for each individual operations like create, insert before, insert after and so on.
Define Node Class
So, first of all, we will define a node class that will store data and the address of the previous and next node, as shown below.
Example
// define Node class
class Node
{
public int data = 0;
public Node prev = null;
public Node next = null;
}In the above code, Node is the name of a class. It contains three instance variables data to store the number, prev and next to store the memory address of the previous and next node objects.
Declare Variables
After defining the Node class, now we will declare the necessary variables required for our program as shown below
Example
node start=null, newnode, temp, rn;
int ch, n, x, c, f;The description of the above variables are as follows.
- start will store the address of the first node in the memory. The default value is None.
- newnode will store the address of newly created node.
- temp will store the address of a selected node for temporary purpose. This variable will be used to reverse the linked list.
- rn will store the address of recent node. This variable will be used when we will read each node one by one.
- ch will store the choice of the menu input by the user like 1, 2, 3, etc.
- n will store the number input by the user and will be used later on in the program for various purposes.
- x will store the number input by the user and will be used later on in the program for various purposes.
- c will be used to count the total number of nodes present in the linked list.
- f will be used to check if a node is found or not. When a node is found in the list the value of f will be 1 otherwise 0.
Add Operation (case 1:)
In the add operation, we will add a new node in the linked list using the program below.
Example
// Enter a number to store in node
System.out.print("Enter a number ");
n=sc.nextInt();
// create a node object in newnode
newnode = new Node();
newnode.data = n;
newnode.prev = null;
newnode.next = null;
if(start == null) // if start in None
{
start = newnode; // then assing the newnode in start (start points to the first node in the memory)
}
else
{
rn=start; // if start is not NULL then assign start in rn to start reading from the first node
// run a while loop until we find null in the next part of rn
while(rn.next != null)
{
rn=rn.next; // if rn->next part is not null then move to the next node
}
rn.next = newnode; // when while loop ends, the rn stands at the last node and we assign the newnode in the next part of the rn
newnode.prev = rn; // newnode->prev = recent node
}
break;Display Operation (case 2:)
In the display operation, we will display all the nodes on the screen using the program below.
Example
if(start == null)
{
System.out.println("List is empty");
}
else
{
rn = start; // recent node
// display the nodes on the screen
while(rn != null)
{
System.out.print(rn.data + " ");
rn=rn.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
break;Insert Before Operation (case 3:)
In the insert before operation, we will insert a new node before a selected node in the linked list using the program below.
Example
f=0;
if(start == null)
{
System.out.println("List is empty");
}
else
{
System.out.print("Insert Number ");
n=sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("Insert Before ");
x=sc.nextInt();
// create a node object in newnode
newnode = new Node();
newnode.data = n;
newnode.prev = null;
newnode.next = null;
// search number x in the list from the starting node
rn=start; // recent node
while(rn != null)
{
if(start==rn && rn.data==x) // insert before first node
{
newnode.next=rn; // newnode->next = recent node
rn.prev=newnode; // recent node->prev = newnode
start=newnode; // start = new node
f=1;
break;
}
else if(start!=rn && rn.data==x) // insert before recent node
{
newnode.next=rn; // newnode->next = recent node
newnode.prev=rn.prev; // new node->previous = recent node->previous
newnode.prev.next=newnode; // new node->previous->next = new node
rn.prev=newnode; // recent node->previous = new node
f=1;
break;
}
rn=rn.next; // recent node = recent node->next
}
if(f==0)
{
System.out.println("Number not found");
// remove the newely created node reference
newnode=null;
}
}
break;Insert After Operation (case 4:)
In the insert after operation, we will insert a new node after a selected node in the linked list using the program below.
Example
f=0;
if(start == null)
{
System.out.println("List is empty");
}
else
{
System.out.print("Insert Number ");
n=sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("Insert After ");
x=sc.nextInt();
// create a node object in newnode
newnode = new Node();
newnode.data = n;
newnode.prev = null;
newnode.next = null;
// search number x in the list from the starting node
rn=start; // recent node
while(rn != null)
{
if(rn.data==x && rn.next==null) // insert after last node
{
newnode.prev=rn; // newnode->previous = recent node
rn.next=newnode; // recent node->next = newnode
f=1;
break;
}
else if(rn.data==x && rn.next!=null) // insert after recent node
{
newnode.next=rn.next; // newnode->next = recent node->next
newnode.next.prev=newnode; // new node->next->previous = newnode
newnode.prev=rn; // new node->previous = recent node
rn.next=newnode; // recent node->next = new node
f=1;
break;
}
rn=rn.next; // recent node = recent node->next
}
if(f==0)
{
System.out.println("Number not found");
// remove the newely created node reference
newnode=null;
}
}
break;Count Operation (case 5:)
In the count operation, we will count the total numbers of nodes present in the linked list using the program below.
Example
c=0;
if(start == null)
{
System.out.println("List is empty");
}
else
{
// count from the first node till last node
rn=start; // recent node
while(rn != null)
{
c=c+1;
rn=rn.next; // recent node = recent node->next
}
System.out.println("Total Nodes = " + c);
}
break;Search Operation (case 6:)
In the search operation, we will search if a given node is present in the linked list using the program below.
Example
f=0;
c=0;
if(start == null)
{
System.out.println("List is empty");
}
else
{
System.out.print("Enter Number to Search ");
x=sc.nextInt();
// search number x in the list from the starting node
rn=start; // recent node
while(rn != null)
{
c=c+1; // count the numbers
if(rn.data==x)
{
System.out.println("Number " + rn.data + " Found at Position " + c);
f=1;
break;
}
rn=rn.next; // recent node = recent node->next
}
if(f==0)
{
System.out.println("Number not found");
}
}
break;Delete Operation (case 7:)
In the delete operation, we will delete a given node from the linked list using the program below.
Example
f=0;
if(start == null)
{
System.out.println("List is empty");
}
else
{
System.out.print("Enter Number to Delete ");
x=sc.nextInt();
// search number x in the list from the starting node
rn=start; // recent node
while(rn != null)
{
if(start==rn && rn.data==x) // delete the first node
{
start=rn.next; // start = recent node->next
rn.next.prev=null; // recent node->next->prev = NULL
rn = null; // remove the reference of recent node
f=1;
System.out.println("Number Deleted Successfully");
break;
}
else if(rn.next!=null && rn.data==x) // delete other node
{
rn.prev.next=rn.next; // recent node->previous->next = recent node->next
rn.next.prev=rn.prev; // recent node->next->prev = recent node->previous
rn = null; // remove the reference of recent node
f=1;
System.out.println("Number Deleted Successfully");
break;
}
else if(rn.next==null && rn.data==x) // delete the last node
{
rn.prev.next=null; // recent node->prev->next = null
rn = null; // remove the reference of recent node
f=1;
System.out.println("Number Deleted Successfully");
break;
}
rn=rn.next; // recent node = recent node->next
}
if(f==0)
{
System.out.println("Number not found");
}
}
break;Reverse Operation (case 8:)
In the reverse operation, we will reverse the reading order of nodes in the linked list by changing their pointer direction using the program below.
Example
if(start == null)
{
System.out.println("List is empty");
}
else
{
rn=start; // recent node = start
temp = null; // temp node = null
while(rn!=null)
{
temp = rn.prev; // temp = recent node->previous
rn.prev = rn.next; // recent node->previous = recent node->next
rn.next = temp; // recent node->next = temp
rn = rn.prev; // recent node = recent node->prev
}
start=temp.prev; // start = temp->previous
// print the reverse list
rn=start; // recent node
while(rn != null)
{
System.out.print(rn.data + " ");
rn=rn.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
break;


