Mastering One Dimensional Array in Java Programming
Arrays in Java
This lesson will teach us how to create, manipulate and use One Dimensional Array in Java programming language with In-depth explanations, code examples, and practice lessons.
What is One Dimensional Array (1D Array) in Java?
A One-Dimensional Array in Java programming is a special type of variable that can store multiple values of only a single data type such as int, float, double, char, etc. at a contagious location in computer memory. Here contagious location means at a fixed gap in computer memory.
A One-Dimensional Array is also known as 1D Array.
Suppose we want to store the age of 10 students. In that case, we have to declare 10 variables in our Java program to store the age of 10 students.
Now here comes the use of a one-dimensional array. With the help of 1D Array, we will declare a single variable in our Java program that can store the age of 10 students at a time.
Declaration Syntax of a One Dimensional Array in Java
datatype variable_name[] = new datatype[size];Or
datatype[] variable_name = new datatype[size];Here, size is the number of elements we want to store in the array.
Example
int a[]=new int[5];Or
int[] a=new int[5];Once we declare the 1D Array, it will look like as shown in the picture below:
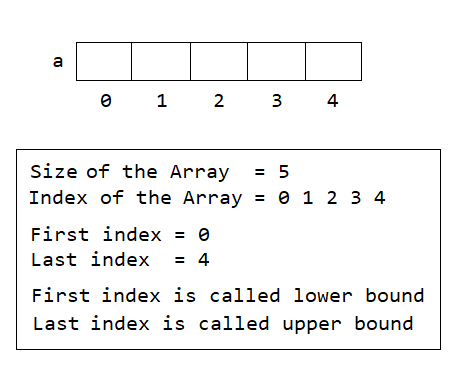
In above image we can see that the name of the one dimensional array is a and it can store 5 integer numbers. Size of the array is 5. Index of the array is 0, 1, 2, 3 and 4.
The first index is called Lower Bound, and the last index is called an Upper Bound. Upper Bound of a one dimensional is always Size – 1.
Declaration and Initialization of a One Dimensional Array in Java
In Java programming a one dimensional array can be declared and initialized in several ways. Let’s see the different ways of initializing a 1D array.
Example 1:
int a[]=new int[] {12,18,6};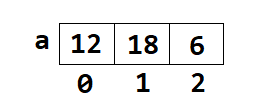
Example 2:
int a[]={7,12,9};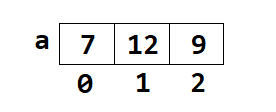
Example 3:
int a[]=new int[3];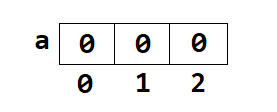
Note: If an array is initialized, without assigning any value, then the default value of each cell of the array will be 0.
Store Numbers in a One Dimensional Array
To store the number in each cell of the array we can use the following syntax.
array_name[index]=value;Example
a[0]=26;
a[1]=15;
a[2]=34;
Access Numbers in a One Dimensional Array
We can access any number stored in a 1D array using the following syntax.
array_name[index];Example
System.out.println(a[0]+" "+a[1]+" "+a[2]);Output
26 15 34
Store and Access the Numbers in a 1D Array using Loops
We can also store as well as access the numbers in a 1D array using either for, while or do while loop. Let's see a few examples.
Example 1
Program to input 10 numbers in an array and display only the even numbers if present in the array.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Example
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a[]=new int[10], i;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter 10 numbers");
for(i=0; i<10; i++)
{
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("List of even numbers");
for(i=0; i<10; i++)
{
if(a[i]%2==0)
{
System.out.print(a[i]+" ");
}
}
}
}Output
Enter 10 numbers 11 15 28 31 49 54 72 81 93 14 List of even numbers 28 54 72 14
Here, you can see that we have run a for loop 10 times to store the user's input in the array. After that we have run another for loop 10 times to access each number from the array and print only the even numbers from it.
Example 2
Program to input 5 numbers in an array and print all the numbers from the backside of the array. Example: 12 18 16 Output: 16 18 12
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Example
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a[]=new int[5], i;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter 5 numbers");
for(i=0; i<5; i++)
{
a[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
for(i=4; i>=0; i--)
{
System.out.print(a[i]+" ");
}
}
}Output
Enter 5 numbers 48 21 97 64 53 53 64 97 21 48
Here, you can see that we have run a for loop 5 times to store the user's input in the array. After that we have run another for loop in reverse order to print all the numbers from the back side of the array.
Test Your Knowledge
Attempt the practical questions to check if the lesson is adequately clear to you.




