Queue using Linked List in Java
Data Structures in Java
In this lesson, we will learn how to implement the queue using a singly linked list in java.
Linked List Implementation of Queue in Java
We know about the queue and how to implement it using an array. This lesson will teach us how to implement the queue using a singly linked list.
We also know that two operations are possible on the queue, add and delete. See the image below to clearly understand how to implement add and delete operation on a queue using a linked list.
Add Example
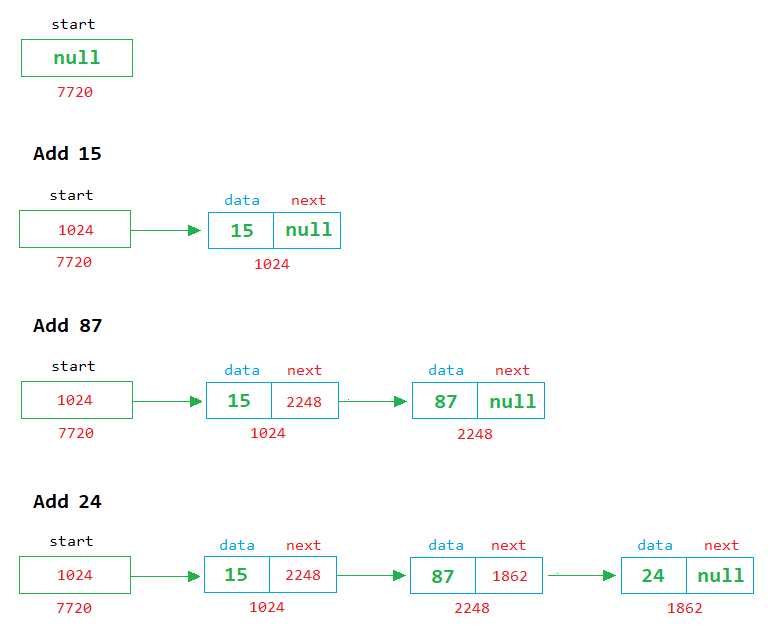
In the above image, we can see that when a new node is created, it is linked with the last node.
Delete Example
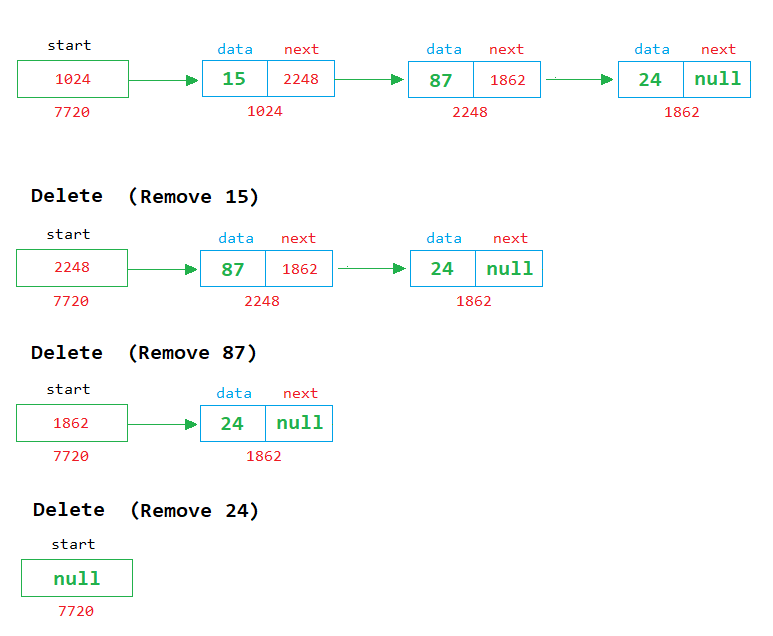
In the above image, we can see that each time a node is removed, the first node is deleted from the list, and the address of the next node is stored in the start variable.
Program of Queue using Linked List
Below is the complete program of queue in java using singly linked list having size 5.
Example
import java.util.Scanner;
// define Node class
class Node
{
public int data = 0;
public Node next = null;
}
public class QueueLinkedList
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node start=null, temp, rn;
int c=0, ch, n, size=5;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
for(;;) // An infinite loop
{
System.out.println("\n1. Add");
System.out.println("2. Delete");
System.out.println("3. Display");
System.out.println("4. Exit");
System.out.print("Enter Choice: ");
ch=sc.nextInt();
switch(ch)
{
case 1:
if(c==size)
{
System.out.println("Queue is full");
}
else
{
// Enter a number to store in node
System.out.print("Enter a number ");
n=sc.nextInt();
// create a node object in temp
temp=new Node();
temp.data=n; // assign the value of n in the data part of temp
temp.next=null; // assign the null in the next part of temp
if(start==null) // if start in null
{
start=temp; // then assing the temp in start (start points to the first node in the memory)
}
else
{
rn = start; // if start is not null then assign start in rn to start reading from the first node
// run a while loop until we find null in the next part of rn
while(rn.next != null)
{
rn=rn.next; // if rn->next part is not null then move to the next node
}
rn.next=temp; // when while loop ends, the rn stands at the last node and we assign the temp in the next part of the rn
}
c++;
}
break;
case 2:
if(start==null)
{
System.out.println("Queue is empty");
}
else
{
System.out.println("Number Popped = " + start.data);
temp=start;
start=start.next;
temp=null; // remove the reference of temp node
c--;
}
break;
case 3:
if(start==null)
{
System.out.println("Queue is empty");
}
else
{
temp=start; // start from 1st node
// display the nodes on the screen
while(temp!=null)
{
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp=temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
break;
case 4:
System.exit(0);
break;
default:
System.out.println("Wrong Choice");
}
}
}
}


